Question Answers
Circular Motion
1. Explain the significance of the banking of a curved road.
When a vehicle moves around a curved road, it requires centripetal force. When the curved roads are banked, the normal reaction of the ground on the vehicle is tilt towards the centre of the curved road as shown in figure. So that, its inward horizontal component can supply the required centripetal force for the motion of the vehicle on the curved road. So, the curved roads are banked.
Here, $$(R_1 + R_2) sin \theta = \frac{mv^2}{r}$$
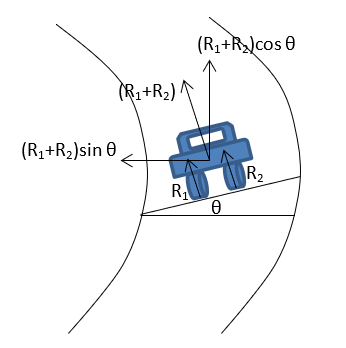
2. Why does a cyclist lean from vertical while turning on curved road path?
When a cyclist turns on a curved path, it leans towards the center of the circular path. Thus, the normal reaction of the ground on the cyclist is tilted with the vertical and its horizontal component is directed towards the center of the circular path. This component provides the necessary centripetal force for the motion of the cyclist.
3. The positively charged nucleus of an atom attracts the electrons in the orbit. Why do electrons not collapse into the nucleus?
The positively charged nucleus of an atom attracts the electrons revolving in the orbit. During its circular motion it also experiences a tendency to move tangentially in a straight line due to its inertia of direction. The inward moving tendency due to centripetal force is balanced by this outward tendency. So, the electrons moves in the orbit and do not collapse into the nucleus.
4. What is the source of centripetal force to a satellite revolving round the earth?
The required centripetal force for the circular motion of a satellite revolving round the earth is provided by the gravitational attraction force between the earth and the satellite. Hence, the gravitation force is the source of centripetal force to the satellite.
5. When a bus takes a turn, passengers are thrown away from the center of the curved path. Why?
When a bus takes a turn, centripetal force acts on the bus towards the center of the circular path. But the passengers tends to be in its initial motion in straight line due to inertia and thus experience an outward force away from the center of the curved path. Hence, passengers are thrown away.
6. Moon is a satellite. But we feel weightless ness in the artificial satellite and some weight on the moon. Why?
Satellite revolves around the earth with the centripetal force provided by the force of gravitation attraction between the earth and the satellite. Weight on the satellite is due to gravitational force of the satellite on the object. Since, the mass of the artificial satellite is small, we feel weightless ness. But the mass of the moon is comparatively large and hence we feel weight on the moon.
7. In washing machine, there is spin dryer, which removes the water from clothes easily. What could be its working principle? Justify.
When the clothes along with water molecule are in circular motion in spin dryer, an outward force acts pushing them to the walls of the dryer. The force continues to act on them even when the clothes have reached the end of the walls. The water molecules in the cloth manages to escape through the holes in the walls of the dryer leaving the clothes waterless and dry.
8. If there is a net force acting on a particle in uniform circular motion, why does the particle’s speed not change?
When a particle is in uniform circular motion, a centripetal force acts on it in the direction towards the center of the circular path. Thus, the direction of the force is perpendicular to the direction of the motion or velocity of the particle. Now, the component of the force towards the direction of the velocity is
$$F_\perp = F cos 90 ^o = 0 $$ Thus, the magnitude of the velocity of the particle is not affected.
9. Explain the difference between a simple and conical pendulum.
A simple pendulum is a heavy point mass object suspended by an inextensible, weightless and flexible string from a rigid support which is free to oscillate in a vertical plane. The time period of simple pendulum is given by,$$T=2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l}{g}}$$ Conical pendulum is a pendulum in which the mass object suspended by a string oscillates in a horizontal plane in such a way that its velocity is in the direction tangential to the horizontal circle. The time period of conical pendulum is $$T=2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l cos \theta}{g}}$$
10. What is meant by angular velocity?
The angular velocity of a body in a circular motion is defined as the time rate of change of angular displacement. It is denoted by ω. Mathematically, $$\omega = \frac{d \theta}{dt}$$ Its unit is radian/sec. Its dimensional formula is $$[M^0L^0T^-1]$$
11. A solid tied at the end of a string is revolved in vertical. At what point the tension in the string will be greatest and the least?
When a solid object of mass m is revolved in a vertical circle of radius r with uniform speed v. At highest point A, $$T+mg = \frac{mv^2}{r}$$ When T is tension on the string, $$\therefore T = \frac{mv^2}{r} - mg .......(1)$$ At lowest point B, $$T-mg = \frac{mv^2}{r}$$ where T is tension on the string, $$\therefore T = \frac{mv^2}{r} + mg ..........(2)$$ From eqn (1) and (2), it is clear that tension is maxium at lowest point and minimum at the highest point.
12. When the motorcyclist is taking a turn with increasing speed, should the angle of inclination with the vertical be increase or decrease?
When a motorcyclist takes a turn, the angle of inclination of the motorcyclist with the vertical is given by $$tan \theta = \frac{v^2}{rg}$$ This shows that, as the speed increases, the angle of inclination should be increased.
13. The moon is accelerating towards the earth. Why isn’t it getting closer to us?
The moon is accelerating towards the earth. During its circular motion it also experiences a tendency to move tangentially in a straight line due to its inertia of direction. The inward moving tendency due to centripetal force is balanced by this outward tendency. Thus the moon moves in a stable orbit and hence it does not get closer to us.
14. Explain why the force of gravity due to Earth does not pull the Moon in closer and closer on an inward spiral until it hit the Earth’s surface?
The moon experiences force of gravity due to earth. During its circular motion it also experiences a tendency to move tangentially in a straight line due to its inertia of direction. The inward moving tendency due to centripetal force is balanced by this outward tendency. Thus the moon moves in a stable orbit and hence it does not get closer to us in an inward spiral path.
15. Why is it more difficult to revolve a stone by tying it to a longer string than by tying it to a shorter string?
The centripetal force acting on a body in circular motion is given by, $$F=m\omega^2 r$$ When a stone is revolved with a longer string, the radius of circular path is large and thus the required centripetal force will large. This centripetal force is provided by the tension produced in the string. If the centripetal force becomes greater than the strength of the string, the string will break and the circular motion ceases. But if a shorter string is used, the required centripetal force will be less and the stone will easily revolve. Hence, it is difficult to revolve a stone by tying it to a longer string than by tying it to a shorter string.