Formulae
Key formulas go here.
Recent Trends in Physics
Seismology
The word 'earthquake' has come from a Greek word 'seismos'. With time, the study of the earthquake became a science and the scientific study of earthquake is called as seismology.
In fact, 'seismology' is the study of 'seismic waves' that are generated at a source within the earth because of natural cause such as movement of tectonic plates of the earth, breaking or collision of rocks inside the earth or due to the artificial cause such as explosion of nuclear bomd. When these seismic wave propragates along the surface or through the inner layer of the earth, we feel a tremor and called it as earthquake. Seismic waves are elastic wave which can propagate through solid and liquid but not through the gas.
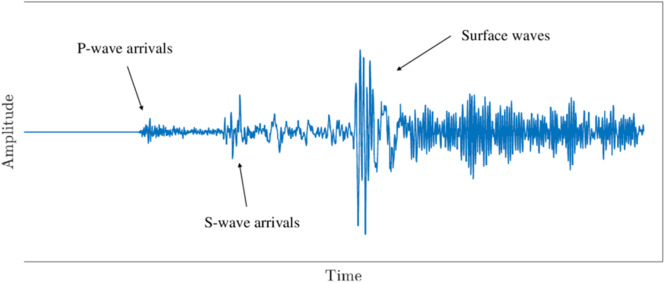
By the study of the seismic waves, we can gather the information about the location and cause of the origin of the earthquake. The device which is used to detect the seismic wave is called as the Seismogram and the magnitude of earthquake is measured in a logrithmic scale called as Reichter Scale.
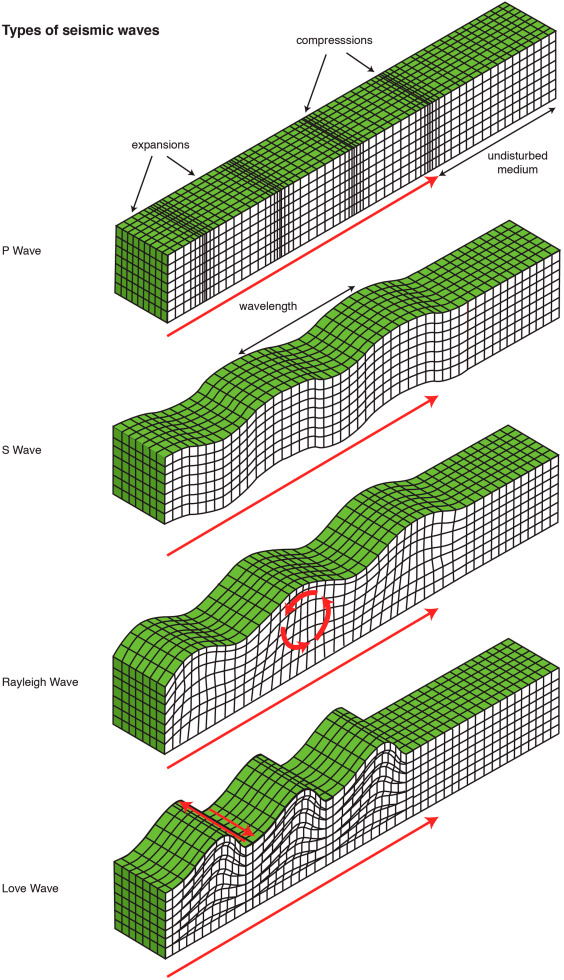
Types of Seismic Waves
On the basis of the path followed by the seismic wave, they are mainly classified as body wave and surface wave.
Body Waves
These are the waves that travel through the interior layers of the earth. It has high frequency and can be longitudinal or transverse.
a. Primary (P) Wave: It is the first wave to be recorded during the earthquake. It propagates at very high speed through the rocks# and fluids inside the earth, during whch it pushes and pulls them in the direction of wave propagation and produces compressions. After earthquake, they spread out inside the volume of the earth and then the amplitude goes on decreasing. Is is also called as the compressive or longitudinal wave.
b. Secondary (S) Waves: It is the second wave to be recorded in the seismic station. It travels much slower than the P wave and can propagate through the solids only as they have shear strength. The particles in this wave, move in the direction perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation. This wave is also known as the transverse or shear wave.
Surface Waves
These waves travel through the surface of the earth like ripple wave in water. As the seismic wave comes to the surface, its frequency decreases. But they have high amplitude, which makes them responsible for the damage and destruction happen on the earth. It is of two types:
a. Love Waves: It is the fastest wave which produces horizontal motion in the earth surface. During this, the ground moves side to side in a horizontal plane but perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation. It damages the foundations of the strucyure and also cause the horizontal shearing on the ground. Like S wave, it doesn't propagate through liquids.
b. Rayleigh Wave: These are the surface wave that produces the ups and downs and side to side movement of the ground in the same direction along which the wave travels. It means, it can move in both horizontal and vertical directions. During the earthquakes, most of the shaking of this wave and it is much larger than any other waves.
Gorkha Earthquake:
Geologists have been grouped Nepal in the high risk zone of earthquake. Recently, Nepal has gone through a devasting earthquake of magnitude 7.8 with the epicenter at Barpark (28.230 /degree N and 84.731 /degre W at depth 8.2 KM) of Gorkha distruct, in 25 April, 2015 at 11:56am Local time. It follows two major after shocks of magnitudes 6.6 and 6.7 withing 24 hours and one major aftershock of magnitude 7.3 after 17 days. The earthquake killed nearly 9,000 people and injured more than 22,000 people. Also, it made huge damages to buildings, infrastructures and many others sectors of mid-Nepal.
According to the US Geological Survey (USGS), the Gorkha earthquake was caused by a sudden thrust or release of built up stress along the major fault line where the Indian plate is slowly diving underneath the Eurasia plate. At the epicenter, it is observed that the Indian plate is converging with Eurasia plate at the rate of 45mm/year towards the north-northeast and a fraction of which (about 18mm/year) is driving the uplift of the Himalayan region.
Gravitational Wave
Gravitational waves are invisible ripples or disturbances in the curvature of space-time that propagates gravity and are generated generated by accelerated masses that propagates as waves outward from their source at the speed of light.
It is the effect of matter on space-time which is produced in the cataclysmic events such as collision of two massive black holes, or supernovae or neutron starts. The existence of the gravitational waves was first proposed by Henri Poincare in 1905 and predicted by Albert Einstein in 1916 in his theory of relativity and its first direct observation was made by LIGO (LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY) in February 11, 2016.
According to the General Theory of Relativity, the field where the heavenly bodies lies is the space-time field and the field is more curved near the massive objevts, i.e., the curvature of space-time is determined by the distribution of masses and the motion of the mass fluctuates the curvature. When two massive starts collide, it produces huge distortion in the fabric of space-time and the large amount of energy produced moves outward in the form of gravitional waves which transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radient energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. In the case of observed binary system (Hulse-Tylor Binary Pulsar in 1974) the orbital period was found to reponsible for it.
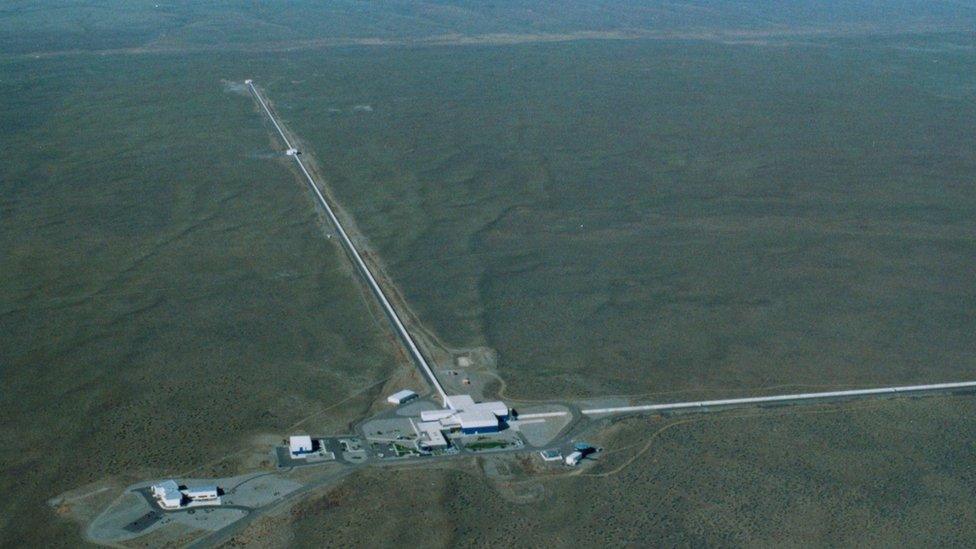
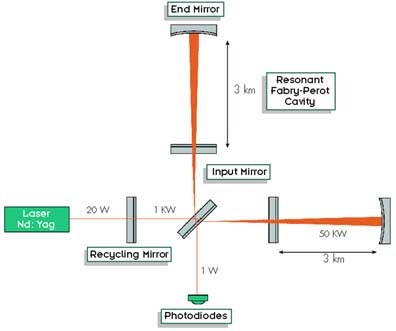

In LIGO, the detectors use laser interferometry to measure the small ripples in the space time caused by passing gravitational waves produced by cosmic events. The variations of gravitational field are transmitted from place to place as electromagnetic waves. The first direct detection of the gravitational wave in LIGO was due to merger of two black holes (about 29 and 36 times bigger than the sun situated at about 1.3 billion light years away). Even the merger was extremely energetic, the wave become so weak (~10-3 times the size of nucleus) when reaches to the earth.
Nanotechnology
The physical and chemical properties of matter change at extremely low level, in the range of nano-scale (~10-9m). Nanotechnology (nano-tech or nano-science) refers to the designing, producing, using structures, devices and systems by manipulating atoms or molecules at the scale of 1 to 100 nano-meters, or even less. In other words, nanotechnology is the engineering of functional system at the molecular scale. Generally it deals withe the structure of size 100nm or smaller and involves developing materials and devices within that size.
Nanotechnology has the potential to create many new materials and devices within that size.
1. Nano medicine diagnosis, drugs delivery and tissue enginnering.
2. Catalysis, nano filteration in the field of chemistry.
3. ICs, semiconducting devices, quantum computers, etc.
4. Production of low power consuming devices.
5. Constructions, refineries, aerospace, manufacturing industries, etc.
Higgs' Boson
Higgs bosons are the elementary particles which are responsible for the mass of any matter in the universe. In the standard model of elementary particles physics, the particles like electrons and quarks are taken as the building block of all the matters and the Higgs boson gives mass to such individual particles. The Higgs bosons are produced by the quantum excitation of the Higgs field.
It was named after physicist Peter Higgs, who lead a team of five physicists and proposed a mechanism in 1964 to find out why the particles have mass. A particles's mass determines how much it resists the changing of its speed or position when it encounters a force. They proposed a boson responsible for the mass of any matter, which is called as the Hiigs' Boson.